‘Coral Persistence Despite Marginal Conditions in the Port of Miami’
Friday, April 28th, 2023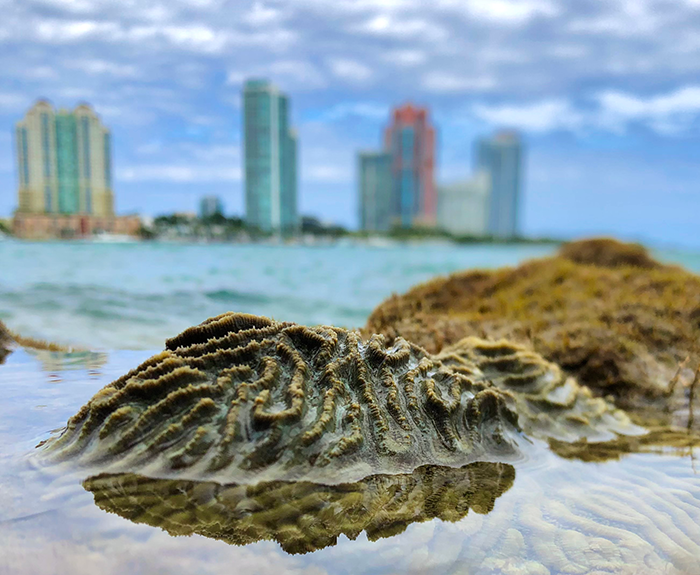
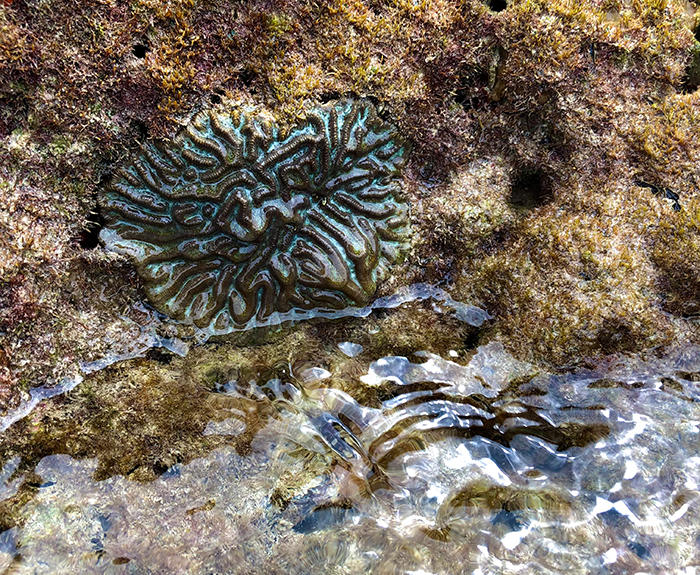
Symmetrical Brain Coral (Pseuododiploria strigosa) emersed during low tide along the shoreline of PortMiami.
In a new paper published in the research journal Scientific Reports, ‘Coral persistence despite marginal conditions in the Port of Miami‘, the monitoring of sites throughout the Port since 2018 revealed periodic extremes in temperature, seawater pH, and salinity, far in excess of what have been measured in most coral reef environments. Despite conditions that would kill many reef species, we have documented diverse coral communities growing on artificial substrates at these sites—reflecting remarkable tolerance to environmental stressors. Furthermore, many of the more prevalent species within these communities are now conspicuously absent or in low abundance on nearby reefs, owing to their susceptibility and exposure to stony coral tissue loss disease.
As we hypothesized in 2014 and evidenced by our recent findings, Miami’s system of urban waterways provides an inadvertent anthropogenic laboratory whose corals hold keys to understanding how the world’s coral reefs might adapt to changing climate and water chemistry in the decades to come.
Read ‘Coral persistence despite marginal conditions in the Port of Miami‘:
URBAN-CORAL-PAPER-2023-s41598-023-33467-7
Read news coverage on the paper from the Miami Herald and WLRN Miami.